Heat Transfer Coefficient Sheet Metal

Heat transfer engineering and design engineering metals and materials thermal conductivity heat transfer review.
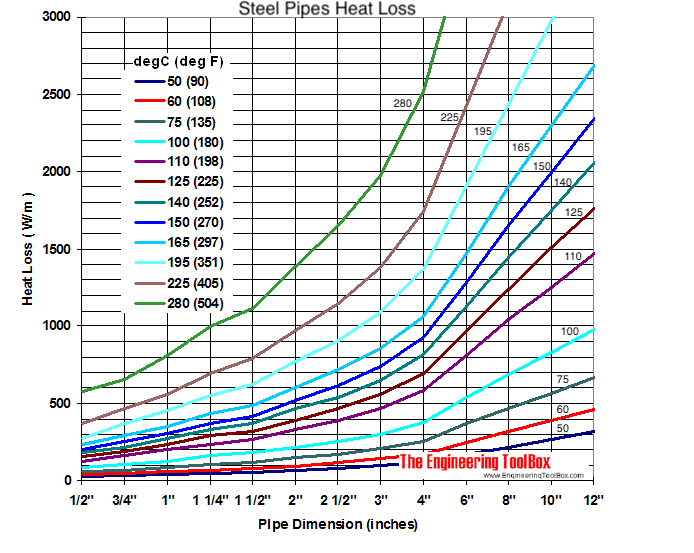
Heat transfer coefficient sheet metal. H q ts k. Other influences include the temperature difference across the metal the thickness of the metal and the surface area of the metal. U the overall heat transfer coefficient w m 2 k btu ft 2 h o f. Calculate conductive heat transfer.
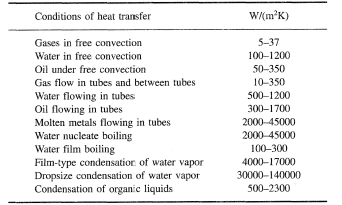
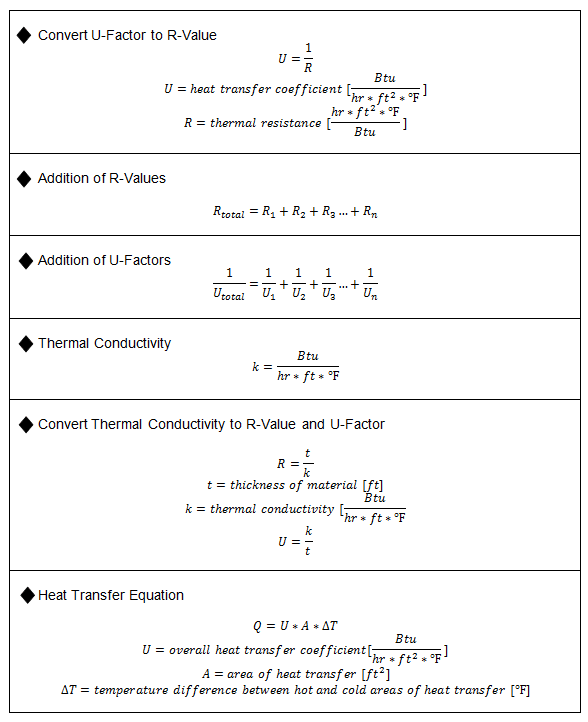
The heat transfer coefficient is the proportionality coefficient between the heat flux and the thermodynamic driving force for the flow of heat i e the temperature difference δt. Heat transfer coefficient on air side h a 0 04 w 0 cm 2 conductivity k of steel 60 w mk at given temperature range solution. Thermal conductivity k is the quantity of heat transmitted due to an unit temperature gradient in unit time under steady conditions in a direction normal to a surface of the unit area. The overall heat transfer coefficient for a multi layered wall pipe or heat exchanger with fluid flow on each side of the wall can be calculated as.
At room temperature iron has a thermal conductivity of 73 but at 1832 f its conductivity drops to 35. Overall heat transfer coefficient for a heat exchanger is a proportionality constant used to calculate overall heat transfer rate between two bodies arising from the temperature difference between those two bodies. Typically they are malleable and ductile deforming under stress without cleaving. For example the initial temperature of the metal can make a huge difference to its heat transfer rate.
Metals in general have high electrical conductivity high thermal conductivity and high density.